Imagine being able to create a lifelike, detailed image from a basic sketch or a clear, high-quality picture from a hazy snapshot. Image-to-image translocation lets us accomplish exactly this. This novel technology transforms one kind of image into another using artificial intelligence (AI). The possibilities are great, from improving medical imaging to producing breathtaking game visual effects.
This technology is changing our interaction with images, whether it's turning a daytime scene into a night-time one or translating satellite images into more useable forms. Thanks to contemporary algorithms like GANs, image-to-image translation is becoming more potent and easily available. It opens interesting prospects for sectors including entertainment, healthcare, and art.
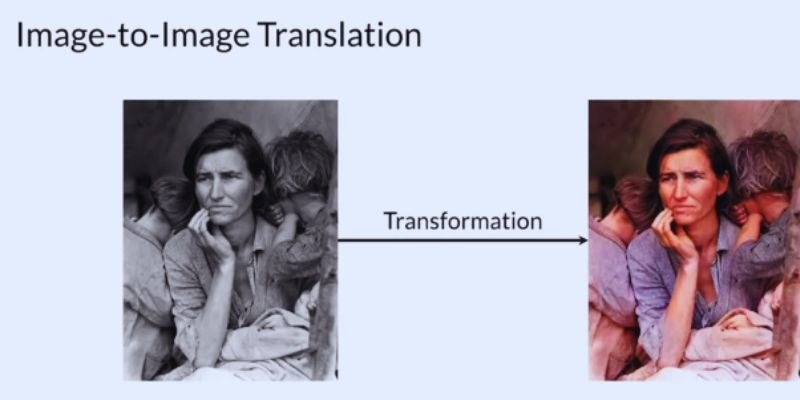
What Is Image-to-Image Translation?
Inspired by learned patterns, image-to-image translation is an artificial intelligence technique wherein one type of image can be converted into another. While maintaining important characteristics, it transforms a picture from a source domain into a target domain. It can, for instance, transform a daytime picture into a twilight one or take a drawing and create a realistic photograph. Deep learning techniques, which examine and learn the links between paired images, drive this process.
The method generates realistic, accurate outputs by first using patterns found in the training set and then applying them to fresh photos. Image-to-image translation is widely used in fields like computer vision, digital art, and healthcare. It helps manipulate and enhance images in ways that were once hard or time-consuming. A breakthrough in picture alteration has occurred since the technology developed, and its uses keep growing in many sectors.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Their Role
Image-to-image translation depends critically on generative adversarial networks (GANs), which offer the fundamental architecture guiding the transformation process. Two neural networks—the generator and the discriminator—make up GANs. The discriminator assesses images produced by the generator from random inputs, deciding whether they are real or phony. These two networks continually improve one another in a competitive environment.
While the discriminator is more adept at differentiating fake from real photos, the generator gets better at producing realistic ones. This adversarial process lets the model generate more lifelike and accurate images. GANs are trained on coupled datasets in the framework of image-to-image translation, hence learning the mapping between input and output images. It makes them perfect for jobs including translating sketches into images, improving image quality, or developing new artistic styles.
Applications of Image-to-Image Translation
Image-to-image translation finds many useful artistic uses in several sectors. In the field of art and design, it saves time and increases inventiveness by enabling artists to transform crude sketches into polished, realistic representations. Graphic designers might use technology, for instance, to create realistic depictions of ideas, including building plans and fashion designs. Image-to-image translation is used in the healthcare industry to improve medical imaging by means of scan quality enhancement. Improved diagnosis and therapy preparation depends on this.
Image-to-translation is applied in the entertainment sector, particularly in film and video game development, to create realistic textures, environments, and visual effects, thus enhancing general production quality. It also finds use in disciplines like satellite photography, where low-quality aerial images are improved for better analysis and decision-making. As technology develops, its applications will keep growing, and new opportunities will be opened.
How Image-to-Image Translation Works?
Deep learning systems analyzing vast collections of paired images to learn the correlations between them enable image-to-image translation. The first training for the model uses a dataset where every input image corresponds to a target image. A daytime picture might have a similar midnight picture. The model learns in training how to map features from the input image to the target domain. The model may create fresh images following learned patterns once trained.
The technique relies heavily on convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to extract important features from images. Once trained, the model can turn a new input image into one that matches the style of the target domain. The degree of training quality of the model, the volume of data, and the complexity of the intended output will determine how well the transformation succeeds.
Challenges in Image-to-Image Translation
Image-to-image translation presents various difficulties, even with its developments, that could compromise the realism or quality of the images that are produced. Ensuring the produced image looks as authentic as possible is one of the toughest challenges, particularly considering intricate transformations like turning a sketch into a realistic picture. The outcome would be unrealistic if the model occasionally fails to make artifacts or maintain important information.
Large and varied datasets are another difficulty since the success of the model mostly relies on the quality of the data. Moreover, it is computationally costly and time-consuming, so training these models calls for strong hardware and large resources. Furthermore, managing variances in style, lighting, and texturing, particularly in cases when the input and output domains are somewhat diverse, challenges the process.
The Future of Image-to-Image Translation
With ongoing developments in AI and ML stretching the bounds of what is feasible, image-to-image translation looks bright. The ability to create reasonable, high-quality photos from many sources will only rise as technology develops. More sophisticated models—such as deep convolutional networks and upgraded GAN architectures—are projected to increase picture translation task accuracy and efficiency.
In sectors like healthcare, this might entail more accurate medical imaging, so supporting earlier discovery and improved therapy. In the creative and entertainment spheres, it will allow ever more lifelike visual effects and quicker manufacturing techniques. Smaller companies and developers will also find this technology more approachable if it allows transformations with less data and fewer resources.
Conclusion:
Image-to-image translation is transforming many sectors, offering fresh means of image manipulation and enhancement. From enhancing medical scans to turning sketches into lifelike images, its uses are many. Even if maintaining realism and handling big datasets remain difficult, developments in artificial intelligence—especially with GANs—keep enhancing the technology. As the process gets better, industries, including design, entertainment, and healthcare, could be changed. Image-to-image translation has bright prospects since it offers unique and pragmatic solutions that will help businesses all around, thereby improving efficiency, innovation, and creativity in hitherto unheard-of degrees.











