The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation with the rapid advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI plays a crucial role in developing autonomous vehicles, enabling them to drive safely without human intervention.
Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and General Motors are pushing the boundaries of self-driving technology, aiming to make transportation more efficient, safe, and accessible. AI-powered vehicles rely on machine learning, sensors, and advanced computing systems to navigate roads, recognize obstacles, and respond to real-time traffic conditions.
The Role of AI in Autonomous Vehicles
AI is the backbone of self-driving technology. It helps vehicles understand their surroundings, make decisions, and navigate roads efficiently. The core AI technologies in autonomous vehicles include:
- Machine Learning (ML): Vehicles learn from vast amounts of data to improve driving accuracy and decision-making. It allows them to recognize road signs, pedestrians, and lane markings.
- Computer Vision: Vehicles use huge amounts of data to learn how to drive better and make better decisions. They can see road signs, people walking, and lane lines better.
- Neural Networks: AI uses real-time info to make split-second choices about how to drive. These networks keep getting better as new data and drive trends come in.
- LiDAR and Radar Systems: These technologies map surroundings, detect distances, and recognize obstacles in all weather conditions, providing a complete view of the environment.
- Sensor Fusion: AI takes data from many devices and puts it all together to get a full and accurate picture of the road, traffic, and surroundings.
Without AI, self-driving cars would not be able to work safely and adjust to changing road conditions. These systems work together to make vehicles more automated and cut down on mistakes made by people.
How AI Powers Autonomous Driving
Artificial intelligence (AI) lets cars drive themselves by doing complicated jobs that normally require human intelligence. Artificial intelligence (AI) in self-driving cars depends on three main things: sensing, decision-making, and control.
Perception
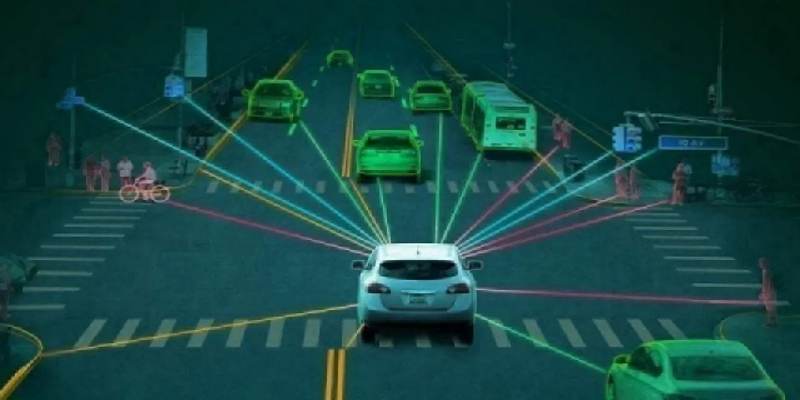

The perception system is responsible for gathering data from sensors, cameras, and radars. AI interprets this data to detect:
- Other vehicles, cyclists, and pedestrians
- Traffic lights, stop signs, and road markings
- Lane boundaries and road curvature
- Weather conditions and road surface quality
By processing and classifying this information, AI ensures the vehicle has an accurate picture of its surroundings.
Decision-Making
Once the AI system has analyzed the environment, it must decide on the best course of action. The decision-making process involves:
- Predicting the movement of other vehicles and pedestrians
- Determining when to accelerate, brake, or change lanes
- Responding to sudden road hazards or obstacles
- Following traffic laws and signals
AI continuously evaluates these factors to ensure safe navigation, avoiding collisions and traffic violations.
Control
The final stage of AI-driven autonomy is vehicle control. AI translates decisions into physical actions such as steering, braking, and accelerating. By integrating AI with the vehicle’s control system, autonomous cars execute commands smoothly and efficiently.
Levels of Autonomy in Self-Driving Cars
Autonomous vehicles are categorized into different levels based on their capability to drive independently. These levels are defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE):
- Level 0 (No Automation): The driver has full control over the vehicle.
- Level 1 (Driver Assistance): AI assists with steering or braking but requires human intervention.
- Level 2 (Partial Automation): Vehicles can control speed and steering but need a driver’s supervision.
- Level 3 (Conditional Automation): AI takes control in some situations but requires human oversight.
- Level 4 (High Automation): Fully automated driving in specific conditions, such as mapped city roads.
- Level 5 (Full Automation): No human intervention is needed, and the vehicle can drive in all environments.
Currently, most available autonomous vehicles operate at Level 2 or Level 3, but advancements are continuously improving their reliability and efficiency.
Benefits of AI-Powered Self-Driving Cars
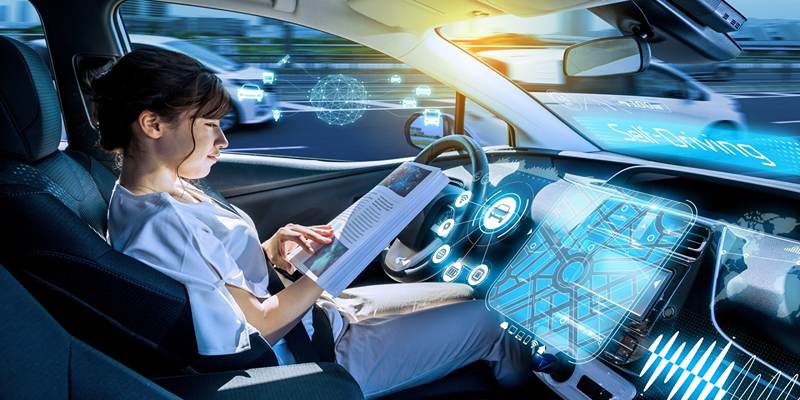

The integration of AI in autonomous vehicles provides numerous advantages, including:
- Enhanced Safety: AI reduces human errors, which cause most accidents. The technology ensures vehicles follow traffic laws and react to hazards in milliseconds.
- Reduced Traffic Congestion: AI-driven cars communicate with one another, optimizing traffic flow and reducing bottlenecks.
- Lower Fuel Consumption: AI optimizes driving efficiency, reducing fuel and energy usage.
- Better Road Efficiency: AI-driven vehicles maintain optimal speeds, reducing delays and improving overall traffic movement.
- Consistent Driving Behavior: Unlike human drivers, AI-powered vehicles do not experience fatigue, distractions, or emotional driving responses.
As AI technology advances, the overall impact on road safety and efficiency continues to improve.
Challenges in Implementing AI in Autonomous Vehicles
Despite the rapid progress, several challenges must be addressed before self-driving cars become mainstream:
Safety and Reliability
Ensuring that AI can handle all road situations safely is a major concern. Self-driving cars must be tested under extreme conditions to guarantee reliability. AI needs to be trained to handle unpredictable road scenarios, such as sudden lane changes, construction zones, and unexpected pedestrian behavior.
Ethical Considerations
Autonomous vehicles must make difficult decisions in critical situations, such as choosing between two potential hazards. Developing ethical AI frameworks is essential for responsible decision-making.
High Development Costs
Building and maintaining AI-powered vehicles require substantial investment, making widespread adoption slow and expensive. The cost of sensors, computing power, and software development remains a barrier.
Conclusion
AI is revolutionizing the automotive industry by enabling self-driving cars to navigate roads safely and efficiently. The combination of machine learning, computer vision, and sensor fusion allows autonomous vehicles to process complex traffic scenarios and make intelligent driving decisions. While there are still challenges in reliability, legal frameworks, and public trust, AI-powered vehicles continue to improve. With continuous technological advancements, AI-driven transportation is becoming a reality, bringing safer and more efficient mobility to the world.